Chlamydia
Chlamydiae are a group of intracellular organisms closely related to Gram-negative bacteria. They grow in eukaryotic cells causing a wide range of diseases in humans, birds and animals.
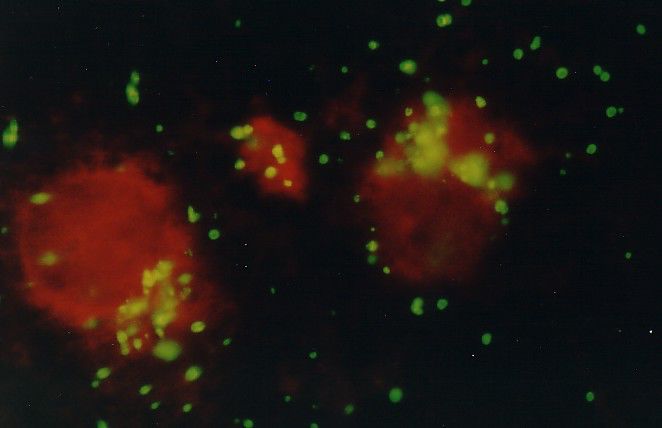
Chlamydia trachomatisThis species is the most important human pathogen amongst the chlamydiae. There are numerous serotypes causing ocular, respiratory and genital illnesses. Coined the "silent infection", asymptomatic individuals continue to live a normal life without knowing they are infected, making the identification of asymptomatic individuals challenging for prevention programmes. Screening has been shown to be an effective method for identification and treatment of asymptomatic individuals because left untreated, can result in the costly treatment of the sequelae of the disease. Detection of C. trachomatis can be made using the Cellabs monoclonal antibody-based direct immunofluorescence assay, Chlamydia Cel IFA. This product provides a quick and convenient way of testing for C.trachomatis, providing the user with microscopy results in just 30 minutes. |
|
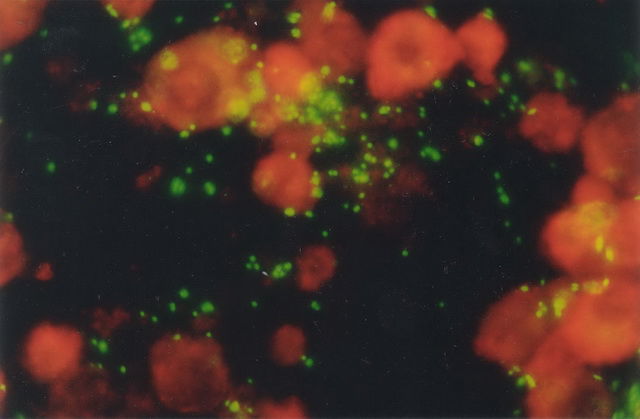
Chlamydia pneumoniaeThis organism causes significant acute respiratory infections in humans, accounting for 10 % of community-acquired pneumonia and 5% of pharyngitis, bronchitis and sinusitis. The infection can be severe in children and the elderly. Detection of C. pneumoniae may be made using the Cellabs monoclonal antibody-based indirect immunofluorescence assay, Chlamydia Cel Pn. |
Image: Chlamydia pneumoniae |
Other Chlamydia species
The species of Chlamydia psittaci has a wide host range in most birds and animals. There are over 50 strains found in about 130 bird species, including parrots, pigeons, doves and ostriches. Avian chlamydiosis also causes acute or chronic disease in poultry, cattle, sheep, and goats resulting in abortion, arthritis and pneumonitis, leading to commercial losses in the meat industry. Transmission of C. psittaci from birds to humans causes psittacosis (ornithosis) resulting in severe pneumonia.
Chlamydia pecorum is a species established in 1992. It consists of bovine, ovine and swine strains formerly classified as C. psittaci. Clinical infections involve the central nervous, respiratory and digestive systems. Many animals remain carriers after recovery.
Chlamydia Group Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
Chlamydia Group LPS can be found in all species of Chlamydia, including those listed above. In Australia, much of the diagnostic studies of chlamydia occurring in Koalas were done using the Chlamydia CEL LPS. Cellabs provides a monoclonal antibody-based direct immunofluorescence assay, the Chlamydia Cel LPS for the detection of Chlamydia Group LPS.